|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
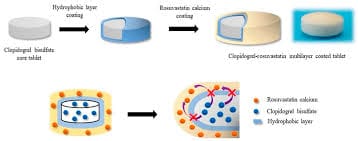
Types of Tablet Coating Processes
Tablet coating processes are vital in the pharmaceutical industry, providing a variety of functional and aesthetic benefits to tablets. These processes enhance the appearance, taste, stability, and controlled release of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). In this article, we explore the most common types of tablet coating processes, each offering unique benefits for different pharmaceutical applications.
1. Film Tablet coating processes
Film coating is one of the most widely used and effective techniques for coating tablets. This process involves applying a thin polymeric layer over the tablet or particulate material. Film coatings are primarily used to enhance the tablet’s appearance, provide controlled drug release, and protect sensitive APIs from environmental factors like moisture and light.
Advantages of Film Coating:
- Efficiency and Speed: Compared to traditional sugar coating, film coating is quicker and requires less operator skill.
- Uniformity: The coating process results in a smooth, even layer, enhancing tablet appearance.
- Minimal Size Change: Tablets coated with film coating retain the same size, structure, and mass as the original compressed tablet.
- Properties of Ideal Film Coating Material:
- Solubility for appropriate use
- Aesthetic appeal with a glossy finish
- Stability against heat, light, and air
- Pleasant odor and taste
- Non-toxic nature
- Compatibility with other coating materials
- Printability for high-speed machines
- Easy application without bridging or filling configurations
2. Sugar Coating
Sugar coating is a traditional method that has been used for many years. This process involves several steps, with the goal of covering the tablet with a shiny, smooth, and attractive sugar-based coating. While more time-consuming compared to other techniques, sugar coating is still favored for its ability to mask unpleasant tastes and odors in medications.
Steps in Sugar Coating:
- Sealing: The sealing or seal coating prevents moisture from penetrating the tablet core, which could lead to softening or disintegration of the tablet.
- Sub-coating: This step adds an additional layer to round the edges of the tablet and increase its size. Sugarcoating can increase the tablet’s weight by 50–100%.
- Syrup Coating (Smoothing/Color Coating): A syrup is applied to smooth out small holes on the tablet surface and add color. This requires skilled personnel to achieve a uniform layer.
- Finishing: The temperature is reduced, and several coats are applied to the tablets to achieve the desired finish.
- Polishing: The final step involves polishing the tablets to achieve the required luster using powdered wax.
Advantages:
- Provides a glossy and elegant appearance
- Masks undesirable flavors and odors
- Enhances patient compliance
3. Gelatin Coating
Gelatin coating is a technique in which one or more layers of gelatin are applied to the tablets, either as printed or unprinted coatings. This method is often used for soft gels or for coating tablets that are difficult to swallow.
Advantages of Gelatin Coating:
- Swallowing Ease: Gelatin-coated tablets are easy to swallow, making them ideal for patients who struggle with traditional tablets.
- Tamper Resistance: The gelatin coating can be used to prevent counterfeiting and improve the security of the medication.
- Taste Masking: Gelatin coatings effectively mask unpleasant tastes and odors.
- Stability Enhancement: Gelatin helps to improve the stability of light-sensitive APIs.
- Clinical Trial Use: Gelatin-coated tablets are commonly used in double-blind clinical trials due to their neutral appearance.
4. Enteric Coating
Enteric coating refers to a coating applied to tablets or capsules to prevent them from dissolving in the acidic environment of the stomach. The coating material is designed to break down in the more neutral or alkaline environment of the small intestine, allowing for targeted drug release.
Advantages of Enteric Coating:
- Protection from Stomach Acidity: Many drugs are sensitive to the acidic pH of the stomach and may degrade before they reach the intestine. Enteric coatings protect the active ingredient from stomach acids.
- Improved Drug Absorption: This method ensures that drugs are released in the small intestine, where they can be absorbed more effectively.
- Ideal for Sensitive Medications: Enteric coatings are used for drugs like insulin that can be degraded in the stomach.
5. Compression Coating
Compression coating involves the application of a coating material to a tablet through compression. The process begins by forming a small tablet using a punch, followed by placing the tablet under a larger punch. The cavity of the die is filled with the coating material, and the entire tablet is compressed.
Advantages:
- Precise Coating Application: Compression coating ensures that the tablet is evenly coated, which is essential for controlled-release formulations.
- Ideal for Combination Drugs: This method is often used to create combination tablets, where the coating protects one active ingredient from being released prematurely.
6. Electrostatic Coating
Electrostatic coating is a unique process in which charged particles are applied to a tablet’s surface. In this method, an electrostatic charge is applied to the tablet, and a coating material containing oppositely charged particles is sprayed onto it.
Advantages:
- Uniform Coating: Electrostatic coating helps achieve a uniform coverage, including difficult-to-reach corners and edges of the tablet.
- Reduced Wastage: The use of charged particles ensures that the coating material adheres to the tablet without excessive wastage.
- Highly Controlled: The electrostatic charge offers more precise control over the coating process, especially for delicate or irregularly shaped tablets.
7. Aqueous Film Coating
Aqueous film coating involves applying a water-based coating solution to the tablet, forming a thin, uniform layer that covers the entire surface. This process is often used as an alternative to organic film coatings that require solvents.
Advantages:
- Environmentally Friendly: Aqueous coatings eliminate the need for organic solvents, making them a more eco-friendly option.
- Safety: Aqueous coatings reduce the exposure of operators to potentially hazardous solvents.
- Uniform Coating: The water-based solution ensures that a uniform coating is applied to the tablets, ensuring consistent quality.
8. Organic Coating
Organic coating refers to the use of natural organic materials, such as plant or animal-based substances, to coat the tablets. These materials are non-synthetic and offer an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic coatings.
Advantages:
- Natural Ingredients: Organic coatings are derived from plant or animal sources, making them more suitable for food supplements or multivitamin tablets.
- Biodegradable: Organic coatings are biodegradable and offer a sustainable alternative to synthetic coatings.
- Gentle on Sensitive Ingredients: Organic coatings are often used for tablets containing sensitive active ingredients like vitamins or minerals.
9. Dip Coating
Dip coating is a traditional coating method in which tablet cores are dipped into a coating solution, allowing the material to adhere to the surface. This method can be repeated several times to achieve the desired coating thickness.
Advantages:
- Simple and Cost-Effective: Dip coating is relatively simple and low-cost compared to other coating techniques.
- Multiple Coating Layers: The process can be repeated multiple times to build up the coating, ensuring a thorough coverage.
Disadvantages:
- Slower Process: Dip coating is slower and less efficient than methods like spray coating.
- Inconsistent Coating: Achieving a uniform coating may be challenging, particularly for tablets with irregular shapes.
10. Vacuum Film Coating
Vacuum film coating involves applying a coating to tablets in a vacuum environment. This method uses a specially designed chamber where the tablets are placed under a vacuum, and coating material is applied in a controlled manner.
Advantages:
- Efficient Coating Process: The vacuum environment accelerates the evaporation process, making the coating process faster and more efficient.
- Minimal Solvent Use: This method reduces the amount of solvent required for the coating process, making it more environmentally friendly.
- High-Quality Coating: The vacuum system ensures that the coating is applied uniformly, producing a high-quality finish.
Conclusion
Tablet coating processes are a critical part of pharmaceutical manufacturing, offering a range of benefits such as improved drug release control, enhanced stability, and better patient compliance. From the traditional sugar coating to modern techniques like electrostatic coating and vacuum film coating, each method serves a specific purpose depending on the medication’s requirements. By choosing the right coating process, pharmaceutical companies can enhance the effectiveness, safety, and appeal of their products while ensuring optimal drug delivery.











Leave a Reply