|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready... |
The Fascinating Process Behind Tablet Manufacturing: Exploring the Rotary Tablet Press
Rotary Tablet Press: Have you ever wondered how those perfectly shaped pills you find in your medicine bottles are made? From a pile of fine powder to a precisely compressed tablet, it seems like magic. But behind this transformation lies an intricate process powered by a piece of machinery known as the rotary tablet press. If you’ve ever been curious about how these machines work, get ready to explore the fascinating world of tablet production.
The Basics of Rotary Tablet Presses
In the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries, rotary tablet presses are vital pieces of equipment used to manufacture tablets. These machines are designed to compress powdered or granular substances into tablets, ensuring each one is of consistent size, weight, and strength. Their widespread use in mass-producing medications, dietary supplements, and vitamins makes them indispensable in the modern pharmaceutical industry.
The rotary tablet press offers high-speed production capabilities, and it operates with precision, making it the preferred choice for large-scale tablet manufacturing. The machine is called “rotary” because it uses a rotating turret to form the tablets, a process that sets it apart from other methods.
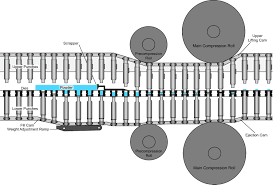
Understanding the Key Components
A rotary tablet press is made up of several essential components that work together to form tablets. Let’s break down the machine’s core parts:
- Turret: This is the rotating part of the machine that holds multiple punches and dies. The turret rotates continuously, and as it does, punches enter the die cavities to compress the material into tablets.
- Punches: These are the tools that compress the powder or granules inside the dies. There are two types of punches: upper and lower. The upper punch descends to apply pressure, while the lower punch assists with ejection.
- Dies: The die is the mold that shapes the tablet. Each turret is equipped with several dies, allowing for the simultaneous production of multiple tablets in each rotation.
- Hopper and Feed Frame: The hopper is where the raw materials (powder or granules) are loaded, and the feed frame ensures that these materials are evenly distributed into the dies.
- Compression Zone: This is where the material is compacted into tablets through the application of pressure by the punches.
- Ejection System: Once the tablet is formed, it is ejected from the die cavity by the lower punch.
Step-by-Step Process of Rotary Tablet Press Operation
Now that we’ve covered the essential components, let’s take a deeper dive into how a rotary tablet press works, from the moment raw materials enter the machine to when the finished tablets are ejected.
- Filling Stage
The first step in tablet production is filling the dies with the powdered or granular material. The material is stored in a hopper, and it flows into the feed frame. The feed frame ensures that the material is evenly distributed into each die cavity. This is crucial because even distribution guarantees uniform tablet weight and quality.
To maintain consistent powder flow, modern rotary tablet presses use sophisticated feeding mechanisms, which may include vibration or augers to move the powder accurately. Proper filling is essential for preventing issues like overfilling or underfilling, which could result in poorly formed or defective tablets.
Image Suggestion: A diagram showing the hopper, feed frame, and die cavities, illustrating the filling process.
- Metering Stage
In the metering stage, the machine controls the amount of material that is dispensed into each die cavity. This is done through a metering mechanism that ensures a precise amount of material is fed into the cavity. After the material is filled, excess powder is removed to ensure each cavity is filled to the correct level.
Accurate metering is critical to maintaining tablet uniformity. Without it, the tablets could vary in weight and potency, leading to product quality issues. The metering system also ensures that there is no wastage of material, thus optimizing efficiency.
Image Suggestion: A close-up shot of the metering stage showing how the material is leveled off before compression.
- Compression Stage
Once the material is properly metered, it moves to the compression stage. This stage consists of two key steps: pre-compression and main compression.
- Pre-Compression
Pre-compression is the first part of the compression process. In this step, the upper punch descends to apply a moderate level of pressure to the powder in the die cavity. The goal of this initial step is to compact the material into a dense mass known as a “slug.”
The pre-compression phase is important because it helps remove air pockets and ensures the material is evenly compacted before the main compression step. This reduces the chances of defects such as cracks or weak points in the final tablet.
Image Suggestion: A diagram or image showing the punches and dies during the pre-compression phase, illustrating how the material is compacted.
- Main Compression
After the pre-compression phase, the upper punch continues its descent and applies a higher level of force to compress the slug into the final tablet shape. The punches work together—while the upper punch applies downward force, the lower punch helps with the upward force to maintain the tablet’s integrity.
The main compression stage determines key tablet characteristics such as hardness, thickness, and density. The force applied during this phase is adjustable, allowing manufacturers to control the tablet’s final properties based on the product’s specifications.
Image Suggestion: A visual showing both punches in action during the main compression stage.
- Ejection Stage
Once the tablet is formed, it is ejected from the die cavity. This is done by the lower punch, which rises to push the tablet out of the die. To ensure that the tablet doesn’t stick to the die and is ejected smoothly, lubricants are often used during the ejection phase.
Some advanced rotary tablet presses are equipped with reject systems that automatically sort out any defective tablets. These defective tablets could be caused by under-compression, over-compression, or other issues during the manufacturing process. A reject system ensures that only high-quality tablets are sent to the next stages of production.
Image Suggestion: An image showing the lower punch pushing the tablet out of the die and the reject system sorting defective tablets.
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Rotary Tablet Press
Operating a rotary tablet press is a delicate process that requires precision. Below is a general Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the proper operation of a rotary tablet press, which ensures that tablet manufacturing is done safely and efficiently.
- Machine Setup
- Cleaning: Before starting, thoroughly clean the machine to remove any residue from previous runs.
- Safety Check: Verify that all safety features, such as emergency stop buttons and safety guards, are in place and functioning.
- Adjustments: Ensure that the machine is set to the desired tablet specifications, including weight, thickness, and hardness.
- Material Preparation
- Raw Material Inspection: Ensure that the raw materials meet the required specifications and have passed quality control checks.
- Formulation Preparation: Prepare the material according to the specific formulation outlined for the product.
- Calibration and Configuration
- Set Machine Parameters: Adjust settings such as turret speed, compression force, and tablet thickness based on the product requirements.
- Calibration: Perform necessary calibration procedures to ensure the machine is accurately set up.
- Machine Operation
- Start the Machine: Power on the machine and let it warm up. Monitor the operation closely during the production process.
- Material Loading: Load the material into the hopper and ensure the feed frame is distributing the material evenly into the dies.
- Monitor Production: Watch the machine as it goes through the filling, metering, compression, and ejection stages. Make adjustments as needed.
- Cleaning and Maintenance
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the machine regularly to avoid contamination and maintain hygiene standards.
- Maintenance: Perform routine maintenance tasks such as lubrication and inspection of critical components.
- Documentation
- Batch Records: Maintain accurate records of batch production, including tablet specifications and machine settings.
- Quality Control: Document tablet quality parameters such as weight, hardness, and dimensions for each batch.
- Shutdown Procedure
- Power Off: Follow proper shutdown procedures to ensure the machine is safely powered off after use.
- Post-Operation Check: Inspect the machine after shutdown to confirm that all tasks were completed.
The Role of Rotary Tablet Presses in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The rotary tablet press is an essential machine in the pharmaceutical industry, enabling the efficient production of tablets with consistent quality. By understanding how these machines work and adhering to proper operating procedures, manufacturers can ensure the production of safe, effective medications and supplements.
In today’s fast-paced pharmaceutical industry, where precision and efficiency are key, the rotary tablet press has become an indispensable tool. Its ability to produce large volumes of tablets quickly and accurately ensures that pharmaceutical companies can meet global demand while maintaining the highest standards of quality control.
Final Thoughts: Rotary tablet presses are marvels of engineering that make possible the mass production of tablets. Whether you’re manufacturing a common over-the-counter medicine or a specialized supplement, understanding how these machines work allows you to optimize your manufacturing processes and deliver high-quality products to consumers worldwide.
Image Suggestion: A high-quality photo of a rotary tablet press in a real-world pharmaceutical setting.
This expanded explanation provides a thorough overview of rotary tablet presses and the critical role they play in pharmaceutical manufacturing. Through step-by-step explanations, visual suggestions, and additional technical insights, we’ve deepened the understanding of this remarkable machine.